Editor’s Note – HPE Ezmeral Container Platform is now HPE Ezmeral Runtime Enterprise. For more information on why the name was changed, please click here.
What is DataTap?

Handling different protocols of file systems is always a pain for a data analyst. DataTap is a file system connector that aims to alleviate this pain. DataTap provides HDFS protocol abstraction that allows big data applications like Spark to run unmodified with fast access to data sources other than HDFS, i.e. HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric XD (formerly named MapR-FS/XD) and GCS (Google Cloud Storage). Using DataTap, you can unify your code while the underlying data sources can be swapped from HDFS, MapR-FS. This flexibility allows developers like you to focus more on coding rather than the underlying infrastructure. More information on DataTap can be found here.
In this blog, I will introduce two ways to access DataTaps in Kubernetes clusters managed by HPE Ezmeral Container Platform deployed with a pre-integrated HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric. The first method covers how to access the DataTaps using HDFS Commands and the second focuses on directly reading data from Apache Spark (using pyspark). Here we go!
Enable DataTap when creating KubeDirector App
First and foremost, you have to enable DataTaps while creating a KubeDirector app. This can be done by ticking the "Enable DataTap" box.

This will result in mounting a lot of files to /opt/bdfs/ of your pod. If you can see the files in your pod (as shown in the image below), it means that your pod is DataTap enabled and you are now ready to access the files in DataTap.
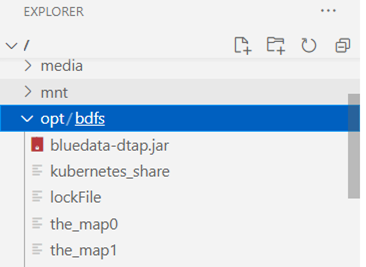
The generic approach can be summarized into these two steps:
- Add
/opt/bdfs/bluedata-dtap.jarto the classpath. - Configure Hadoop with the following values.
name | value |
| fs.dtap.impl | com.bluedata.hadoop.bdfs.Bdfs |
| fs.AbstractFileSystem.dtap.impl | com.bluedata.hadoop.bdfs.BdAbstractFS |
| fs.dtap.impl.disable.cache | false |
Note: fs.dtap.impl.disable.cache can be designated as an option.
Reference: Accessing DataTaps in Kubernetes Pods
Uniform Resource Identifier
In HPE Ezmeral Container Platform, you can see different types of file systems used by the shared storage resources. You can manage different data sources through a GUI while representing files with the same URI. The URI will be in the format of
dtap://datatap_name/some_subdirectory/another_subdirectory/some_fileScreenshot | Description |
 | You can manage different data source whether they are in MapR filesystem or HDFS. |
 | You can add new DataTap with this screen. |
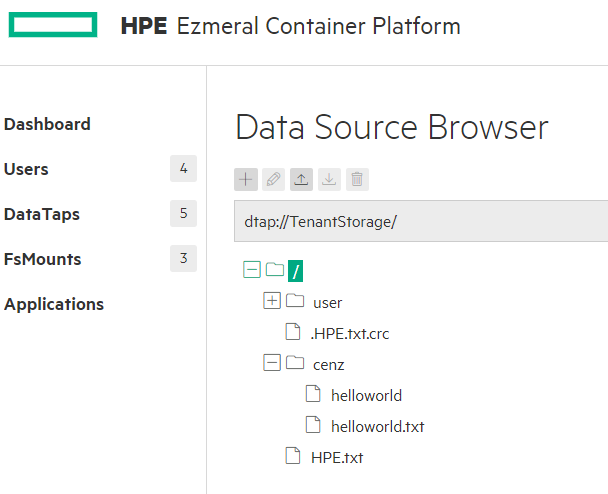 | You can upload, delete or rename files using GUI. |
Access DataTaps using HDFS commands
Introduction
The Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS) is the key component of the Hadoop ecosystem. HDFS commands, of course, are the commands that are responsible for manipulating files for HDFS.
To use the HDFS commands, first you need to start the Hadoop services using the following steps:
Prepare Hadoop
Some of the KubeDirector App provided by HPE is pre-installed a well-configured Hadoop for you. Hence, the following installation steps can be skipped.
Install OpenJDK and the dependency
apt update && apt upgrade -y apt install wget -y # install openjdk DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install openjdk-11-jdk-headless -y
Download Hadoop and untar Hadoop
You can always find the latest version of Hadoop on Apache Hadoop Releases.
wget https://apache.website-solution.net/hadoop/common/hadoop-3.3.0/hadoop-3.3.0.tar.gz # Download Hadoop binary tar zxf hadoop-*.tar.gz # Untar Hadoop binary mv hadoop-3.3.0 $HOME/hadoop # Rename and move Hadoop folder to $HOME cd $HOME/hadoop # Move directory to hadoop
Configure the required environment
In $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh file, assign the following environment variables ($JAVA_HOME, $HADOOP_HOME, $HADOOP_CLASSPATH):
# These two variables is needed for HDFS command. Located at line 54, 58. export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/ export HADOOP_HOME=$HOME/hadoop # This variable is DataTap specific. Located at line 126. export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=$HADOOP_CLASSPATH:$HADOOP_HOME/lib/:/opt/bdfs/bluedata-dtap.jar
In $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml file, configure Hadoop with the following values:
<configuration> <property> <name>fs.dtap.impl</name> <value>com.bluedata.hadoop.bdfs.Bdfs</value> </property> <property> <name>fs.AbstractFileSystem.dtap.impl</name> <value>com.bluedata.hadoop.bdfs.BdAbstractFS</value> </property> <property> <name>fs.dtap.impl.disable.cache</name> <value>false</value> </property> </configuration>
Alternative
I have prepared an example configuration file on Github. If your Hadoop does not have a special configuration, you can simply download and replace your existing configuration file.
Test your HDFS command
Here are some common commands used to interact with DataTap.
# bash: Current working directory -> $HADOOP_HOME # Check the version of the Hadoop. bin/hadoop version # List the files from the default TenantStorage Data Source. bin/hdfs dfs -ls dtap://TenantStorage/ # Make new directory user in dtap://TenantStorage/. bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir dtap://TenantStorage/user # Move the text files helloworld.txt to "cenz" folder. bin/hdfs dfs -put helloworld.txt dtap://TenantStorage/cenz bin/hdfs dfs -put -f helloworld.txt dtap://TenantStorage/cenz # force replacement # Concatenate a file in dtap. bin/hdfs dfs -cat dtap://TenantStorage/cenz/helloworld.txt # Remove a file in dtap. bin/hdfs dfs -rm dtap://TenantStorage/cenz/helloworld.txt
Tip:
To get rid of the file path
bin/, we can add the Hadoop'sbinandsbinfile to$PATHexport HADOOP_HOME=$HOME/hadoop export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin:$HADOOP_HOME/binReference: Hadoop File System Shell Document
Access DataTaps using pyspark
Introduction
PySpark is an interface for Apache Spark in Python. Apache Spark is a unified analytics engine for big data processing, with built-in modules for streaming, SQL, machine learning and graph processing. Apache Spark can access data from HDFS and, with the extension, file systems managed by DataTap.
Install pyspark
There are lots of ways to install Spark. The simplest way is to install the pyspark package directly using pip install pyspark. Run the following to install the prerequisite packages and pyspark.
# install pyspark & Java apt-get install python3 -y apt-get install python3-pip -y DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install openjdk-11-jdk-headless -y pip install pyspark
There are two ways to interact with pyspark. The first one is to execute the pyspark command in bash to initiate the pyspark session. The second way is that to treat pyspark as a module that the python kernel can import to. (import pyspark)
Method one
Initiate pyspark session with jars
In order to use datatap with pyspark, you have to add an external jar file as an argument to pyspark. Initiate Spark's interactive shell in python using the following command.
# bash # Specify the path of the jars files pyspark --jars /opt/bdfs/bluedata-dtap.jar
After starting the interactive shell, Spark Context and Spark Session are automatically initiated for you.

After specifying the Hadoop configurations, you can read files from DataTap just like you normally did with HDFS.
# pyspark # Specify the Hadoop configurations. sc._jsc.hadoopConfiguration().set('fs.dtap.impl', 'com.bluedata.hadoop.bdfs.Bdfs') sc._jsc.hadoopConfiguration().set('fs.AbstractFileSystem.dtap.impl', 'com.bluedata.hadoop.bdfs.BdAbstractFS') # Commands for reading DataTap file text = sc.textFile("dtap://TenantStorage/HPE.txt") text.take(5)

Method two
Initiate python and initiate pyspark with jars at runtime
Run the Python Shell first:
# bash python3
At the Python runtime, add the path of the jar file using the Spark configuration command:
# python from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext # Specify the path of the jars files. conf = SparkConf().set("spark.jars", "/opt/bdfs/bluedata-dtap.jar") sc = SparkContext( conf=conf) # Specify the Hadoop configurations. sc._jsc.hadoopConfiguration().set('fs.dtap.impl', 'com.bluedata.hadoop.bdfs.Bdfs') sc._jsc.hadoopConfiguration().set('fs.AbstractFileSystem.dtap.impl', 'com.bluedata.hadoop.bdfs.BdAbstractFS') # Commands for reading DataTap file text = sc.textFile("dtap://TenantStorage/HPE.txt") text.take(5)
References:
Conclusion
A distributed file system is fundamental for handling large amounts of data. Managing those file systems tends to always be a pain for developers. DataTaps unify different storage resources into a path that different clusters can use. This helps you to get rid of time-consuming copies or transfers of data. More time spent on extracting business insight from your data and less time handling tedious stuff - that's what DataTap can give you. And that's what you get with HPE Ezmeral.